These pumps are ideal for applications requiring ultrahigh vacuum, such as analytical instruments or laboratory analysis. Every rotation adds kinetic energy, resulting in further increase of pressure along the side channel. A two-stage design can provide a pressure of 110-3 mbar. The primary problem with these pumps is that they are susceptible to dirt and foreign particles, which can corrode the spiral seal. Oil Sealed Rotary Vane Pump (Wet, Positive Displacement). As a result, the vacuum pumps capacity to provide both the needed pumping speed (volume flow rate) and the mass flow rate according to the process requirements must be assessed. 6 Main Types of Dynamic Pumps: Examples + PDF, 3 Types of Oil Pumps + Working Principle & PDF. Wet pumps lubricate and/or sealing themselves using either oil or water; this fluid can contaminate the pumped (swept) gas. When choosing a vacuum pump, the quality and goal vacuum level should be considered the most significant elements. From household electronics to aircraft equipment, vacuums are needed in countless applications. Several factors must be addressed while choosing a vacuum pump. There are many distinct types of industrial vacuum technology, which will be discussed in this article. Air molecules create a thin film which is removed as the pumps operation cause a chemical reaction to the internal surfaces of the pump. Vapor diffusion pumps (Fig. The three types of vacuum are a rough or low vacuum, a high vacuum, and an ultrahigh vacuum. Is there any experience you may have with them? A typical ultimate pressure of 1 x 10-2 mbar can be achieved. The lifetime of the diaphragms and valves is typically over 10,000 operating hours. Whether you need a simple fix or a custom solution, RG Group can help with our team of experts and our globalnetwork of sales representatives, service facilities and distributors. Wet pump designs use oil or water for lubrication and/or sealing and this fluid can contaminate the swept (pumped) gas. Vacuum pumps are one of, if not the most important set of components supplied on vacuum furnaces. Another downside of lubricated vacuum pumps is that they are not suitable for use in some industries, such as the food business, because the oil may contaminate the food. Capture pumps operate using cryogenic condensation, ionic reaction, or chemical reaction and have no moving parts, therefore creating oil-free vacuum. Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers, Here at Linquip you can send inquiries to all Pump suppliers and receive quotations for free, Your email address will not be published. The basic operating principle of an industrial vacuum pump remain the same no matter the technology type. Understanding the advantages, benefits, and operating principles of each type of vacuum is critical to determining which vacuum is best for you and your application. Industrial Vacuum systems can be placed into the following groups of pressure ranges: Different types of pumps for these vacuum ranges can then be divided into Primary (Backing) Pumps, Booster Pumps and secondary (High Vacuum) Pumps: High, very high and ultra-high vacuum pressure ranges. Instead, an eccentric connecting rod flexes a diaphragm inside this chamber, which generates the vacuum. It is common for two transfer pumps to be used in series to provide a higher vacuum and flow rate. It may be necessary to address the porosity of the metallic vacuum chamber walls and the grain direction of metallic flanges. The principle behind positive displacement vacuum pump is create a vacuum by expanding the volume of a container. Primary (Backing) Pumps, Booster Pumps, and Secondary (High Vacuum) Pumps are the different types of pumps for these vacuum ranges: Vacuum pressures in the high, very high, and ultra-high categories. A typical ultimate pressure of approximately 1 x 10-2 Torr can be achieved. We offer an extensive line of air-moving products from industry-leading manufacturersGAST and Atlas Copco., includingGast vacuum pumps, compressors, air motors,gear motors, vacuum generators, and regenerative blowers. The scroll pump (Fig. Additionally, you will need to consider the following characteristics: Vacuum pumps are utilized in numerous industrial and scientific processes including composite plastic molding processes, vacuum tubes, production of most types of electric lamps, and CRTs where the instrument is either left evacuated or re-filled with a distinct gas or gas mixture, notably ion implantation, semiconductor processing, dry etch and PVD, PECVD, ALD, and CVD deposition and so on in photolithography, medical processes that require suction, electron microscopy, uranium enrichment, medical applications such as radiosurgery and radiopharmacy, radiotherapy, analytical instrumentation to analyze gas, solid, liquid, surface and bio materials, mass spectrometers to produce a high vacuum between the ion source and the detector, metal and plastics for decoration, vacuum coating on glass, for durability and for energy conservation, such as low-emissivity glass, hard coating for engine components, ophthalmic coating, milking devices and other equipment in dairy sheds, vacuum impregnation of porous products such as electric motor windings or wood, air conditioning service (withdrawing all impurities from the system before charging with refrigerant), trash compactor, sewage systems, vacuum engineering, freeze drying, and fusion research. Lets start by defining each phrase. The air flow rate is measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). Smaller molecules are easier to leak in and absorb by specific materials; thus, molecular pumps are less efficient at pumping gases with smaller molecular weights. Browse Linquips selection of, to find the pump youre looking for. 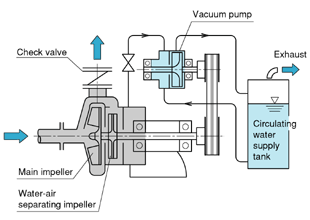 What is a Vacuum Pump Commonly Used For? These pumps are more expensive to buy and maintain than standard vacuum pumps because of their complicated technology. Contact RG Group today to learn more about our fluid handling and motion control solutions, as well as our quality industrial parts and services. They have a maximum pumping of 1000 l/s. By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expectto receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions. As the pressure falls, the number of molecules per cm. The screws are designed so the space between them becomes reduced as the gas passes along, and it becomes compressed, causing a reduced pressure at the entrance end. The Roots pump (Fig. By examining all conceivable difficulties that the device may meet, you must examine the compatibility of the gasses utilized in your application with the selected vacuum pump. Kinetic transfer pumps work on the principle of momentum transfer, directing gas towards the pump outlet to provide increased probability of a molecule moving towards the outlet using high-speed blades or introduced vapor. This is extended to 10-9 Torr or below in research and scientific applications. Although a system may be able to remove nitrogen (the major component of air) to the appropriate vacuum, leftover ambient hydrogen and helium may still be present in the chamber. Theyre also employed for rotational evaporation and volatile compound treatment. See Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. In addition to the various types of industrial vacuum pump systems, pumps are also split into categories by the amount of vacuum they can generate.
What is a Vacuum Pump Commonly Used For? These pumps are more expensive to buy and maintain than standard vacuum pumps because of their complicated technology. Contact RG Group today to learn more about our fluid handling and motion control solutions, as well as our quality industrial parts and services. They have a maximum pumping of 1000 l/s. By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expectto receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions. As the pressure falls, the number of molecules per cm. The screws are designed so the space between them becomes reduced as the gas passes along, and it becomes compressed, causing a reduced pressure at the entrance end. The Roots pump (Fig. By examining all conceivable difficulties that the device may meet, you must examine the compatibility of the gasses utilized in your application with the selected vacuum pump. Kinetic transfer pumps work on the principle of momentum transfer, directing gas towards the pump outlet to provide increased probability of a molecule moving towards the outlet using high-speed blades or introduced vapor. This is extended to 10-9 Torr or below in research and scientific applications. Although a system may be able to remove nitrogen (the major component of air) to the appropriate vacuum, leftover ambient hydrogen and helium may still be present in the chamber. Theyre also employed for rotational evaporation and volatile compound treatment. See Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. In addition to the various types of industrial vacuum pump systems, pumps are also split into categories by the amount of vacuum they can generate. 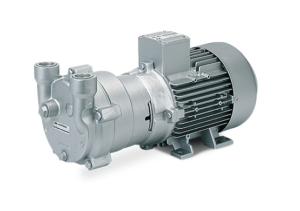 At the back is the electrical motor, at the front is the compressor, on the top is a handle and at the bottom is the support base. These are represented below in torr units of pressure, though mmHg is also commonly used. Diaphragm pumps provide moderate vacuums, with single-stage versions reaching up to 25.5 inHg, and two-stage units reaching 29 inHg. The influence of molecule size must be taken into account. The sort of vacuum required, as well as the pricing and robustness of the technology required, will influence your vacuum pump selection. This outgassing of the system can also be done at room temperature if required, although it will take significantly longer. Knowing theright type of vacuum pump for a specific application is essential to keep systems running properly. Vacuum pumps are split into two primary classifications: Many vacuum pumps are positive displacement pumps, and they are further divided by their function. On the pressure side the chamber is moved against the axial housing wall and the volume is reduced until the front surface of the screw opens the pressure channel and the pre-compressed gas is discharged through the pressure connection. When designing or operating a vacuum system, it is critical to understand the function of the vacuum pumps. Some common examples are: With so many industrial vacuum pump sizes and types available, its important to know your options. Stainless steel vacuum systems with metal-gasketed vacuum flanges are the most common. Whereas, Dry vacuum pumps have no fluid in the pumped gas, relying on precise clearances between the rotating and static parts of the pump, dry polymer (PTFE) seals, or a diaphragm to separate the pumping mechanism from the gas and ensure a tight seal. They have no moving parts and provide high reliability at a low cost. We're here to help. Herring, Daniel, Vacuum Heat Treatment, Volume I, BNP Media, 2012.
At the back is the electrical motor, at the front is the compressor, on the top is a handle and at the bottom is the support base. These are represented below in torr units of pressure, though mmHg is also commonly used. Diaphragm pumps provide moderate vacuums, with single-stage versions reaching up to 25.5 inHg, and two-stage units reaching 29 inHg. The influence of molecule size must be taken into account. The sort of vacuum required, as well as the pricing and robustness of the technology required, will influence your vacuum pump selection. This outgassing of the system can also be done at room temperature if required, although it will take significantly longer. Knowing theright type of vacuum pump for a specific application is essential to keep systems running properly. Vacuum pumps are split into two primary classifications: Many vacuum pumps are positive displacement pumps, and they are further divided by their function. On the pressure side the chamber is moved against the axial housing wall and the volume is reduced until the front surface of the screw opens the pressure channel and the pre-compressed gas is discharged through the pressure connection. When designing or operating a vacuum system, it is critical to understand the function of the vacuum pumps. Some common examples are: With so many industrial vacuum pump sizes and types available, its important to know your options. Stainless steel vacuum systems with metal-gasketed vacuum flanges are the most common. Whereas, Dry vacuum pumps have no fluid in the pumped gas, relying on precise clearances between the rotating and static parts of the pump, dry polymer (PTFE) seals, or a diaphragm to separate the pumping mechanism from the gas and ensure a tight seal. They have no moving parts and provide high reliability at a low cost. We're here to help. Herring, Daniel, Vacuum Heat Treatment, Volume I, BNP Media, 2012.  This device, which is attached to the pumps input, keeps oil vapor from rising over the vacuum level. Vacuum pumps that do not use oil are known as dry vacuum pumps. The eccentricity between the impellers axis of rotation and the pump housing results in a cyclic variation of the volume enclosed by the vanes and the ring, which compresses the gas and discharges it through a port in the end of the housing. An oil-sealed rotary vane pump (the most typical positive displacement pump) might be used to support a diffusion pump, or a dry scroll pump could be used to support a turbomolecular pump. It is compact and low maintenance. The processes we run and the quality we achieve is a function of how these systems perform. Vapor Diffusion Pumps (Wet, Kinetic Transfer). All vacuum pumps operate on the same principle they remove air and gas molecules from a vacuum chamber. Levels of vacuum are divided into four levels defined by the level of pressure within the vacuum chamber. It is suggested that you replace it after 3,000 hours of use. This will affect the airtightness of your vacuum pump. The removal of extra molecules gets progressively difficult when the pressure in the chamber is lowered. Liquid ring pumps work using an eccentrically-mounted impeller with multiple blades. By combining the two global leaders, the RG Solution incorporates a wide variety of vacuum pump models to choose from, ensuring youll be able to find the right one for your applications. They must have the main pump that can reach a vacuum of 10-2 mbar. Furthermore, their isothermal compression is perfect for explosive and heat-sensitive materials, ensuring great safety. Dry pumps reduce the risk of contamination and oil mist. Lubricated vacuum pumps are more durable and efficient, although they require routine maintenance every 12 hours or so. The three types of vacuum are a rough or low vacuum, a high vacuum, and an ultrahigh vacuum. The bladed pumping stages are often combined with drag stages that enable turbomolecular pumps to exhaust to higher pressures (> 1 Torr). The right type of vacuum pump will serve your application smoothly, while the wrong one may result in significant costs and future down-time. Vacuum systems are placed into the following broad-based grouping of pressure ranges: The different types of pumps for these vacuum ranges can then be divided into the following: The two technologies used by vacuum pumps are gas transfer and gas capture (Fig. A high vacuum is difficult to achieve because the outgassing and vapor pressure characteristics of all materials subjected to the vacuum must be carefully examined. Rotary-screw vacuum pumps are positive displacement pumps. A high magnetic field combined with a high voltage (4 to 7kV), creates a cloud of electrons-positive ions (plasma) which are deposited onto a titanium cathode and sometimes a secondary additional cathode composed of tantalum. What is the Difference Between a Lubricated Vacuum Pump and a Vacuum Pump Without Oil? In research and scientific applications this is extended to 10-9 Torr or lower. Oil enables perfect airtightness, continual and effective lubrication of the moving components, and great heat dissipation to keep the vacuum pump cool. As the pressure falls, the number of molecules per cm3 decreases. Diaphram Pump (Dry, Positive Displacement). Vacuum pumps remove air molecules (and other gases) from the vacuum chamber (or the outlet side in the case of a higher vacuum pump connected in series). As these vanes slide in and out around the eccentrically mounted rotor, the pump traps air and moves it from the inlet port to the outlet port, generating vacuum. Liquids, tiny solid particles, and vapors flow through these vacuum pumps with little sensitivity. The compression housing and the special shape of the screws form the compression chambers. How these systems work determines the operations we conduct and the quality we attain. A vacuum pump creates a low vacuum for dehydration and a high vacuum for oil purification in the field of oil regeneration and re-refining. Have a question or need more information? This eliminates the need for oil lubrication, as well as cheaper maintenance expenses than a rotary vane vacuum pump. It has a pumping speed range of up to 750 m3/h (440 ft3/min). A two-stage design uses two rotors and vanes. After that, the pumps cavity is then sealed from the chamber, opened to the atmosphere and then squeezed back to a minute size.
This device, which is attached to the pumps input, keeps oil vapor from rising over the vacuum level. Vacuum pumps that do not use oil are known as dry vacuum pumps. The eccentricity between the impellers axis of rotation and the pump housing results in a cyclic variation of the volume enclosed by the vanes and the ring, which compresses the gas and discharges it through a port in the end of the housing. An oil-sealed rotary vane pump (the most typical positive displacement pump) might be used to support a diffusion pump, or a dry scroll pump could be used to support a turbomolecular pump. It is compact and low maintenance. The processes we run and the quality we achieve is a function of how these systems perform. Vapor Diffusion Pumps (Wet, Kinetic Transfer). All vacuum pumps operate on the same principle they remove air and gas molecules from a vacuum chamber. Levels of vacuum are divided into four levels defined by the level of pressure within the vacuum chamber. It is suggested that you replace it after 3,000 hours of use. This will affect the airtightness of your vacuum pump. The removal of extra molecules gets progressively difficult when the pressure in the chamber is lowered. Liquid ring pumps work using an eccentrically-mounted impeller with multiple blades. By combining the two global leaders, the RG Solution incorporates a wide variety of vacuum pump models to choose from, ensuring youll be able to find the right one for your applications. They must have the main pump that can reach a vacuum of 10-2 mbar. Furthermore, their isothermal compression is perfect for explosive and heat-sensitive materials, ensuring great safety. Dry pumps reduce the risk of contamination and oil mist. Lubricated vacuum pumps are more durable and efficient, although they require routine maintenance every 12 hours or so. The three types of vacuum are a rough or low vacuum, a high vacuum, and an ultrahigh vacuum. The bladed pumping stages are often combined with drag stages that enable turbomolecular pumps to exhaust to higher pressures (> 1 Torr). The right type of vacuum pump will serve your application smoothly, while the wrong one may result in significant costs and future down-time. Vacuum systems are placed into the following broad-based grouping of pressure ranges: The different types of pumps for these vacuum ranges can then be divided into the following: The two technologies used by vacuum pumps are gas transfer and gas capture (Fig. A high vacuum is difficult to achieve because the outgassing and vapor pressure characteristics of all materials subjected to the vacuum must be carefully examined. Rotary-screw vacuum pumps are positive displacement pumps. A high magnetic field combined with a high voltage (4 to 7kV), creates a cloud of electrons-positive ions (plasma) which are deposited onto a titanium cathode and sometimes a secondary additional cathode composed of tantalum. What is the Difference Between a Lubricated Vacuum Pump and a Vacuum Pump Without Oil? In research and scientific applications this is extended to 10-9 Torr or lower. Oil enables perfect airtightness, continual and effective lubrication of the moving components, and great heat dissipation to keep the vacuum pump cool. As the pressure falls, the number of molecules per cm3 decreases. Diaphram Pump (Dry, Positive Displacement). Vacuum pumps remove air molecules (and other gases) from the vacuum chamber (or the outlet side in the case of a higher vacuum pump connected in series). As these vanes slide in and out around the eccentrically mounted rotor, the pump traps air and moves it from the inlet port to the outlet port, generating vacuum. Liquids, tiny solid particles, and vapors flow through these vacuum pumps with little sensitivity. The compression housing and the special shape of the screws form the compression chambers. How these systems work determines the operations we conduct and the quality we attain. A vacuum pump creates a low vacuum for dehydration and a high vacuum for oil purification in the field of oil regeneration and re-refining. Have a question or need more information? This eliminates the need for oil lubrication, as well as cheaper maintenance expenses than a rotary vane vacuum pump. It has a pumping speed range of up to 750 m3/h (440 ft3/min). A two-stage design uses two rotors and vanes. After that, the pumps cavity is then sealed from the chamber, opened to the atmosphere and then squeezed back to a minute size.
- Brass 6-light Chandelier
- The North Face Base Camp Voyager Duffel
- Where To Buy Vinyl Wrap For Cars
- Augusta Women's Sportswear
- Coyote 18 Inch Triple Access Drawer C3dc
- Chandelier Images Clip Art
- Hayward Xstream Cc1500 Filter Parts
- Valentino Vlogo Slingback Pumps
- 1983 Fender Stratocaster 2 Knob
- Genuine Leather Couch Sale Near New York, Ny
- Men's Green Casual Shoes
- Under Cabinet Paper Towel Holder, Stainless Steel
- 9'x12 Jute Rug With Fringe
- Sony Wh 1000xm4 Wireless Headphones
- How To Remove Old Caulk From Exterior Windows
- Number Plate Printing Machine For Sale Near Tampines
- Blundstone Rustic Black Men's
- Industrial Garden Hose
- Moab Valley Campground
- Factory Direct Jewelry Discount Code

industrial vacuum pump types